erythroid|stages of erythropoiesis : Cebu How the erythroid lineage is made has been a topic of intense research over the last decades. Developmental studies show that there are two types of red blood .
webMortal kombat 11. Help / Troubleshooting. So I just got done downloading mk11 off of steamunlocked. I clicked on the mk11 exe application link and my mcafee atinvirus .
0 · what are erythroid cells
1 · stages of erythropoiesis with diagram
2 · stages of erythropoiesis
3 · sites of erythropoiesis
4 · site of erythropoiesis in adults
5 · myeloid vs erythroid
6 · adults erythropoiesis occurs
7 · acute erythroid leukemia survival rate
8 · More
WEBTHE GAME MASTER IS BACK ON THE WIKI. After nearly 1 year of being deleted, The Game Master makes her return to the backrooms wiki in a rewrite, with brand new .
erythroid*******Learn about the differentiation, regulation, and function of erythroid cells, the red blood cells that transport oxygen and carbon dioxide. Explore chapters and articles from various books and journals on erythroid cell biology and pathology.
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (from ancient Greek erythros 'red' and kytos 'hollow vessel', with -cyte translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen (O2) to the body tissues—via . Learn about erythropoiesis, the process of making red blood cells in your bone marrow. Find out how hormones, oxygen levels and diseases affect erythropoiesis .As they mature, a number of erythrocyte characteristics change: • The overall size of the erythroid precursor cell decreases, increasing the cytoplasmic to nucleus (C:N) ratio. The nuclear diameter decreases and chromatin condenses with the staining reaction progressing from purplish red to dark blue at the final nuclear stage of the orthochromatic erythroblast, prior to nuclear ejection.
Control of the erythroid cell cycle. Progression and variation in the cell cycle are crucial for erythropoiesis, because they balance proliferation and differentiation. Cell .erythroidHow the erythroid lineage is made has been a topic of intense research over the last decades. Developmental studies show that there are two types of red blood . Learn about erythrocytes, the anucleate, biconcave cells that transport oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood. Find out their structure, function, life cycle, .
Erythropoiesis is one of the important physiological supply functions of the bone marrow. In healthy adults, about 200×10 9 red cells are produced per day in the . Overview of erythropoiesis, from the hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) to the red blood cell (RBC). Erythropoiesis takes place in the bone marrow, and erythroblastic . How the erythroid lineage is made has been a topic of intense research over the last decades. Developmental studies show that there are two types of red blood cells .
The first identifiable erythroid progenitor, termed “burst-forming unit-erythroid” (BFU-E), is defined by its ability to generate large colonies with scattered clusters of erythroblasts in semi-solid medium. Differentiation of BFU-E produces “colony-forming units-erythroid” (CFU-E) that generate smaller colonies containing about 50 cells.
For a red blood cell to eventually form, an HSC becomes a common myeloid progenitor (CMP) cell. A CMP may mature into a red blood cell, platelet or some types of white blood cells. A CMP that eventually becomes a red blood cell develops into a megakaryocyte-erythroid progenitor cell (MEP).Erythroid lineage potential arises from different progenitor subsets according to revised hematopoietic hierarchy (A) Classical view of hematopoiesis suggests that erythroid progenitors are derived from discrete multipotent progenitors populations that undergo a series of differentiation steps whereby these progenitor cells become increasingly .The erythroid precursor cell compartment, also termed the erythron, includes cells that, in contrast to the erythroid progenitor cells (BFU-E and CFU-E), are defined by morphologic criteria. The earliest recognizable erythroid cell is the proerythroblast, which after four to five mitotic divisions and serial morphologic changes gives rise to .
However, the notion that EPO stimulated-erythroid progenitors may produce factors that influence bone homeostasis has also been proposed (43, 86). The identification of specific factors produced by erythroid progenitors that functionally link erythropoiesis and bone homeostasis would greatly support this hypothesis. How the erythroid lineage is made has been a topic of intense research over the last decades. Developmental studies show that there are two types of red blood cells--embryonic and adult. They develop from distinct hemogenic/hematopoietic progenitors in different anatomical sites and show distinct genetic programs. This article highlights the .
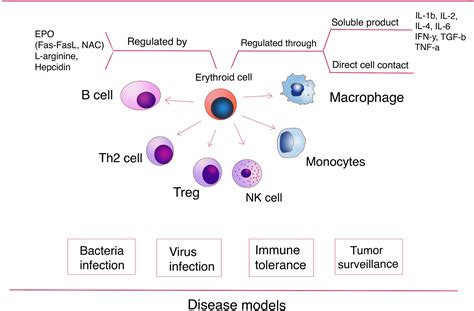
Immunological consequences of extramedullary erythropoiesis: immunoregulatory functions of CD71+ erythroid cells. Immunological consequences of extramedullary erythropoiesis: immunoregulatory functions of CD71 + erythroid cells Haematologica. 2020 Jun;105(6):1478-1483. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2019.243063. . Every second, the human body generates 2 million red blood cells, through the process of erythropoiesis. Human erythropoiesis is a complex, multi-step process, from the multipotent hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) to the mature erythrocyte (Orkin 2000).The first steps of erythroid differentiation involve an engagement phase, in which . Maturation from erythroid-committed precursors is called terminal erythropoiesis and occurs in the BM within erythroblastic islands, which consist of a central macrophage surrounded by erythroblasts, and ends in the blood stream where reticulocytes complete their maturation within 1–2 days. During this phase, proerythroblasts (Pro-E) .

The erythroid terminal differentiation program couples sequential cell divisions with progressive reductions in cell size. The erythropoietin receptor (EpoR) is essential for erythroblast survival .
Abstract. Erythropoiesis is the biological process that consumes the highest amount of body iron for heme synthesis. Heme synthesis in erythroid cells is finely coordinated with that of alpha (α) and beta (β)-globin, resulting in the production of hemoglobin, a tetramer of 2α- and 2β-globin chains, and heme as the prosthetic group.During active erythroid nuclear transcription, increased miR-181a represses Xpo7 expression but during erythroid maturation, Xpo7 expression increases with decrease in miR-181a levels, allowing nuclear condensation to begin followed subsequently by enucleation. In summary, there may be additional miRNAs yet to be identified and . From CMP, a megakaryocytic erythroid progenitor (MEP) (c-kit +, CD34-, CD71 low, CD16/32 - in mice and CD45+, GPA-, IL-3R-, CD34+, CD36-, and CD7 low) will give rise to erythroid progenitors. In another model, there is a debate on whether hematopoiesis does not undergo a hierarchal progression through MPP, long term, or .
Erythroid cells – Although erythroid hyperplasia (associated with ineffective erythropoiesis) is usually seen, red cell aplasia and/or hypoplasia also rarely occur . Morphologic abnormalities in erythroid precursors include large size, nuclear multi-lobation, nuclear budding, and other abnormal forms.Erythroid Cell. Erythroid cells include erythroid precursors in the bone marrow (proerythroblast, basophilic normoblast, polychromatic normoblast, and orthochromatic normoblast) and reticulocytes and erythrocytes present in both the bone marrow and the peripheral bloodstream. From: Total Burn Care (Fourth Edition), 2012Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (from ancient Greek erythros 'red' and kytos 'hollow vessel', with -cyte translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of . Erythropoiesis (pronounced “ur-i-throw-poy-EE-sus”) is your body’s process of making red blood cells (erythrocytes). Erythropoiesis ensures you have the right number of blood cells — not too few or too many. Red blood cells are important because they:
Erythropoiesis (from Greek 'erythro' meaning "red" and 'poiesis' "to make") is the process which produces red blood cells (erythrocytes), which is the development from erythropoietic stem cell to mature red blood cell. [1]How the erythroid lineage is made has been a topic of intense research over the last decades. Developmental studies show that there are two types of red blood cells—embryonic and adult. They develop from distinct hemogenic/hematopoietic progenitors in different anatomical sites and show distinct genetic programs. Control of the erythroid cell cycle. Progression and variation in the cell cycle are crucial for erythropoiesis, because they balance proliferation and differentiation. Cell-cycle regulation is essential to determine the fate of early erythroid progenitors. Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are anucleate, biconcave cells, filled with hemoglobin, that transport oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and tissues. They are produced in the red bone marrow by a process called erythropoiesis.stages of erythropoiesis Erythropoiesis is one of the important physiological supply functions of the bone marrow. In healthy adults, about 200×10 9 red cells are produced per day in the bone marrow and are released into the peripheral blood. 1 Depending on demand, red cell production can be adjusted and upregulated substantially.
webThe Gryphon 2023 - Present 1 Seasons Fantasy List Reviews 90% 100+ Ratings Avg. Audience Score Mark, Memo and Becky come into contact with a fantastic world called the Black Tower.
erythroid|stages of erythropoiesis